本文由 简悦 SimpRead 转码, 原文地址 blog.csdn.net
- 前置说明
本文使用的数据库存储200万行的记录
全文词数:6169
sql文件下载地址:https://gitee.com/alizipeng/the-way-of-programming/blob/master/09-%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93/user.sql
若希望看到其他技术笔记欢迎来访我的技术笔记项目:https://gitee.com/alizipeng/the-way-of-programming
`mysql> select count(*) from user; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 2000000 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.14 sec) mysql> select * from user limit 10; +----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+ | id | name | age | address | birthday | +----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+ | 1 | Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3 | 26 | 云浮市 | 2019-01-13 10:04:55 | | 2 | MrldItwPeb6VDk7zCOO1 | 2 | 汕尾市 | 2018-10-18 09:41:51 | | 3 | 5ag8vXuMnV0JRBH2PKkG | 72 | 梅州市 | 2021-06-16 06:22:28 | | 4 | SccWwgENpikMyriAdJ3V | 12 | 江门市 | 2019-01-17 15:21:14 | | 5 | 96jgKGorO4IQAFg6kIKN | 63 | 深圳市 | 2020-02-25 14:35:45 | | 6 | l8ZJtMI90mfHGTSMcZGm | 15 | 珠海市 | 2019-07-05 12:25:37 | | 7 | ZUu15AfviMv64bI9JGVk | 21 | 东莞 | 2018-12-04 17:18:22 | | 8 | CVXyTqfPgOVPrq2UDPol | 37 | 梅州市 | 2021-03-24 11:51:06 | | 9 | 2sLdyXj6ihbQ2eXUc8n0 | 35 | 河源市 | 2020-11-16 16:39:59 | | 10 | pyM43aO6C24upRSDSMYr | 37 | 湛江市 | 2020-07-27 22:11:45 | +----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+ 10 rows in set (0.00 sec)` ![][img-0] * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * 9 * 10 * 11 * 12 * 13 * 14 * 15 * 16 * 17 * 18 * 19 * 20 * 21 * 22 * 23 * 24
- 索引优化
索引是优化查询最有效的方式之一
# 1.1 是否使用索引的区别
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mnp2PneK-1628668796487)(resource/1628664942206.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6f170a01587841b4a69a2fcdaa38d06d.png)
- 不使用索引
`mysql> select * from user where name = 'Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3';
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | address | birthday |
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| 1 | Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3 | 26 | 云浮市 | 2019-01-13 10:04:55 |
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.55 sec)`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
- 使用索引
`mysql> create index idx_user_name on user(name);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (20.66 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from user where name = 'Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3';
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | address | birthday |
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| 1 | Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3 | 26 | 云浮市 | 2019-01-13 10:04:55 |
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
# 1.2 索引的使用
# 1.2.1 避免索引失效
# 1.2.1.1 建立复合索引
`mysql> create index idx_user_name_age_address on user(name, age, address);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (29.46 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0`
* 1
* 2
* 3
# 1.2.1.2 全值匹配
对索引中所有列都指定具体值,索引生效
`explain select * from user where name='Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3' and age = 26 and address='云浮市';`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-7z0uq5N1-1628668796499)(resource/1628665638188.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cb94f93e5c2348e3bd52336be5a63e0f.png)
# 1.2.1.3 最左前缀法则
如果索引多列,需要遵循最左前缀法则。指查询从索引的最左列顺序开始,不能跳过中间的列
索引生效的情况:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-9vRoiA21-1628668796503)(resource/1628665874239.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5ad6b3986eba4b97bc9e98b3d0d43412.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
索引失效的情况:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TQ8HerYV-1628668796510)(resource/1628666082131.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/da4dbae94b4a4dcf84ade2df128ab9c2.png)
# 1.2.1.4 范围查询
范围查询右边的列不能使用索引
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mOIIahS1-1628668796515)(resource/1628666287071.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e42080bd62e7488997f4c72c952251b8.png)
# 1.2.1.5 运算操作
在索引列上使用运算操作,索引失效
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DhFdLjWb-1628668796520)(resource/1628666470559.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/99d47f1ece264f25bc73774328705f4e.png)
# 1.2.1.6 字符串字段
不加单引号,索引失效【该执行结果使用的是另外的表】
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QREtMnCK-1628668796527)(resource/1628666562405.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d58bc9e89d96440ea9bb418cc461accd.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 1.2.1.7 覆盖索引
尽量使用覆盖索引【索引包含查询列】,减少使用select *
`Extra字段:
using index:使用覆盖索引
using where:使用索引,但需要回表查询
using index condition:使用索引,但需要回表查询
using index; using where:使用索引,需要的字段都在索引中找到,不需要回表查询`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bMxZoity-1628668796532)(resource/1628667048794.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e63f46a7606e419e82f0376474834789.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 1.2.1.8 OR条件查询
若 or 前的条件有索引,后面的列没有索引,则索引全部失效
`explain select * from user where name = 'Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3' or birthday='2019-01-13 10:04:55';`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-I501Mbzo-1628668796536)(resource/1628667255843.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a7c92220491d480ea5459a21749d24c3.png)
# 1.2.1.9 Like模糊查询
以%开头的Like模糊查询,索引失效
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Hu7eDtwF-1628668796540)(resource/1628667406879.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/636568dd4851456b96fe639819bab8cf.png)
但可以通过覆盖索引解决
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-lDE4h4rT-1628668796543)(resource/1628667492973.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8101d9f50d7641d981b8e6bf60fac562.png)
# 1.2.1.10 全表扫描
若MySQL判定全表扫描将比使用索引更快,则不使用索引
# 1.2.1.11 is [not] null
有时索引失效【根据该字段为null的比例判断】
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dl8p4fUl-1628668796546)(resource/1628667752772.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/620ffeefe67040ab815749ffcaa492f5.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 1.2.1.12 [not] in
// todo
# 1.2.1.13 单列索引和复合索引
尽量使用复合索引,少使用单列索引
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-wbjUissq-1628668796548)(resource/1628668093875.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f66c6ad1e7574957be77fc223fe954fa.png)
复合索引idx_user_name_age_address相当于创建了三个索引:
name
name + age
name + age + address
当创建多个单列索引时,数据库会选择一个最优的索引【辨识度最高】,并不会使用全部索引
# 1.2.2 查看索引使用情况
`show [session|global]status like 'Handler_read%';`
* 1
`mysql> show global status like 'Handler_read%';
+-----------------------+----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------------+----------+
| Handler_read_first | 194 |
| Handler_read_key | 6004303 |
| Handler_read_last | 0 |
| Handler_read_next | 6007205 |
| Handler_read_prev | 0 |
| Handler_read_rnd | 330 |
| Handler_read_rnd_next | 33054118 |
+-----------------------+----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show status like 'Handler_read%';
+-----------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------------+-------+
| Handler_read_first | 1 |
| Handler_read_key | 17 |
| Handler_read_last | 0 |
| Handler_read_next | 16 |
| Handler_read_prev | 0 |
| Handler_read_rnd | 4 |
| Handler_read_rnd_next | 5 |
+-----------------------+-------+
7 rows in set (0.01 sec)` ![][img-1]
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27

# 2.1 优化步骤
# 2.1.1查看SQL执行频率
- show status可以查看数据库的状态信息
session级别显示当前会话的状态信息【默认】global级别显示自数据库上次启动至今的状态信息
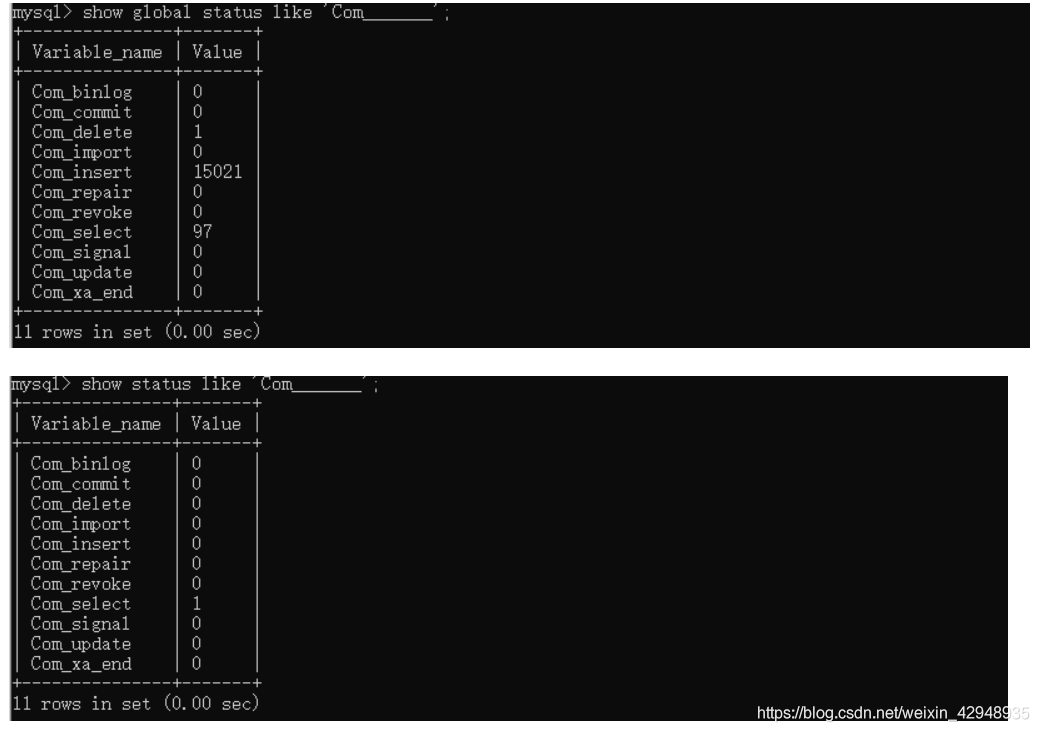
# 2.1.1.1 查看整个数据库CRUD执行频次
`-- 显示增删改查频次,确定数据库是以修改为主还是插入为主
show [session|global] status like 'Com_______';`
* 1
* 2
# 2.1.1.1 查看Innodb存储引擎执行频次
`-- 查看innodb存储引擎的CRUD执行频次
show global status like 'innodb_rows_%';`
* 1
* 2
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-y3jSVZ7A-1628668796558)(resource/1628555264600.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/72683b6b3e1f4311a91cb98a229bff17.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 2.1.2 定位低效率SQL
# 2.1.2.1 慢查询日志定位
慢查询日志记录了索引执行时间超过
long_query_time并且扫描记录数
>=min_examined_row_limit的所有SQL语句的日志
long_query_time默认10秒,最小为0,可以精确到微秒
# 2.1.2.1.1 文件位置和格式
`# 开启慢查询
slow_query_log=1
# 指定慢查询日志文件名
slow_query_log_file=slow_query.log
# 超时阈值
long_query_time=10`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
# 2.1.2.1.2 日志读取
查询long_query_time值
`mysql> show variables like 'long_query_time'; +-----------------+----------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-----------------+----------+ | long_query_time | 1.000000 | +-----------------+----------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)` * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7执行一次慢查询,查看日志
`mysql> select * from user where name like '%Zjcfpe%'; Empty set (1.02 sec)` * 1 * 2`[root@VM-0-6-centos ~]# tail -f /www/server/data/mysql-slow.log /www/server/mysql/bin/mysqld, Version: 8.0.24 (Source distribution). started with: Tcp port: 3306 Unix socket: /tmp/mysql.sock Time Id Command Argument # Time: 2021-08-10T06:35:58.334350Z # User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [] Id: 8 # Query_time: 1.016230 Lock_time: 0.000104 Rows_sent: 0 Rows_examined: 2000000 use myroot; SET timestamp=1628577357; select * from user where name like '%Zjcfpe%';` * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * 9 * 10 * 11读取慢查询文件
`[root@VM-0-6-centos ~]# cat /www/server/data/mysql-slow.log /www/server/mysql/bin/mysqld, Version: 8.0.24 (Source distribution). started with: Tcp port: 3306 Unix socket: /tmp/mysql.sock Time Id Command Argument # Time: 2021-08-10T03:27:52.943049Z # User@Host: myroot[myroot] @ [120.239.131.249] Id: 8 # Query_time: 4.329975 Lock_time: 0.000125 Rows_sent: 27751 Rows_examined: 2000000 use myroot; SET timestamp=1628566068; select * from user where name like '%j5%'; /www/server/mysql/bin/mysqld, Version: 8.0.24 (Source distribution). started with: Tcp port: 3306 Unix socket: /tmp/mysql.sock Time Id Command Argument # Time: 2021-08-10T06:35:58.334350Z # User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [] Id: 8 # Query_time: 1.016230 Lock_time: 0.000104 Rows_sent: 0 Rows_examined: 2000000 use myroot; SET timestamp=1628577357; select * from user where name like '%Zjcfpe%';` ![][img-2] * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * 9 * 10 * 11 * 12 * 13 * 14 * 15 * 16 * 17 * 18 * 19
# 2.1.2.1.3使用mysqldumpslow工具读取
`## 建立软连接
[root@VM-0-6-centos bin]# ln -s /www/server/mysql/bin/mysqldumpslow /usr/bin
[root@VM-0-6-centos bin]# mysqldumpslow /www/server/data/mysql-slow.log
Reading mysql slow query log from /www/server/data/mysql-slow.log
Count: 2 Time=2.67s (5s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=13875.5 (27751), 2users@2hosts
select * from user where name like 'S'`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
# 2.1.2.2 show processlist定位
适用于实时查看SQL执行情况、线程状态、是否锁表等
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-huff06gN-1628668796560)(resource/1628578720341.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e95e02542fee49b4b3bc8b87e756a9d6.png)
| 列名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| id列 | 用户登录mysql时,系统分配的connection_id,可以使用函数connection_id()查看 |
| user列 | 显示当前用户。如果不是root用户,这个命令只显示用户权限范围内的sql记录 |
| host列 | 显示这个SQL语句是从哪个IP+端口发来的 |
| db列 | 操作的目标数据库 |
| command列 | 当前连接的执行命令,休眠【sleep】查询【query】连接【connect】 |
| time列 | 当前状态的持续时间,秒 |
| status列 | 当前连接的SQL语句的执行状态如executing sending data等 |
| Info列 | 执行的SQL语句 |
执行一次慢查询
同时查看实时情况
# 2.1.3 explain分析SQL
- 当定位到效率低的SQL语句后,可以通过
explain获取SQL的执行计划
# 2.1.3.1 查看执行计划
`expalin select * from user where id = 1000;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-IW4AFti1-1628668796566)(resource/1628579918021.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/697cadaf41864074a7b695468ae28a53.png)
`explain select * from user where name = 'KBmXzR6PoIv6T5NQQ27w';`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KP5owVwO-1628668796568)(resource/1628579989186.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/86c41d1a3f944d17917dd398bb05957a.png)
# 2.1.3.2 各字段含义
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| id | select查询的序列号,标识查询中执行select子句或者是操作表的顺序 |
| select_type | Select的类型,常见取值:SIMPLE【简单表,不关联表或子查询】PRIMARY【主查询,外层的查询】UNION【UNION中第二个或后面的查询语句】SUBQUERY【子查询中第一个Select】 |
| table | 输出结果集的表 |
| type | 表连接类型,性能由好到坏【system->const->eq_ref->ref->ref_or_null->index_merge->index_subquery->range->index->all】 |
| possible_keys | 查询时可能使用到的索引 |
| key | 实际使用到的索引 |
| key_len | 索引字段长度 |
| rows | 扫描的行数量 |
| extra | 执行情况的说明和描述 |
# 2.1.3.3 explain之id
- id相同时,表示加载表的顺序是从上到下
`explain select * from sys_role r, sys_user u, sys_user_role ur where r.id = ur.id and u.id = ur.id;` * 1
- id不同,id值越大则优先级越高则越先被执行
`explain select * from sys_role where id = (select role_id from sys_user_role where user_id = (select id from sys_user where username='test'));` * 1
- 相同id与不同id同时存在。相同id则可以归为一组,从上往下执行;在所有组中,id值越高,优先级则越大,则越先被执行
# 2.1.3.4 explain之select_type
常见取值
| select_type | 含义 |
|---|---|
| SIMPLE | 简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或UNION |
| PRIMARY | 查询中若包含任何复制子查询,则最外层标记为PRIMARY |
| SUBQUERY | 在Select或where子句中包含子查询 |
| DERIVED | 在FROM子句中包含的子查询,MySQL递归执行这些子查询,把结果放入临时表 |
| UNION | 若第二个SELECT出现在UNION之后,则标记为UNION; 若UNION包含在FROM子句的子查询中,外层Select将被标记为DERIVED |
| UNION RESULT | 从UNION表获取结果的SELECT |
SIMPLE例子
`explain select * from user;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Kx1ftyhZ-1628668796575)(resource/1628600781169.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b78208ce969f43b28f6358d64102d453.png)
PRIMARY & SUBQUERY例子
`explain select * from sys_user where id = (select user_id from sys_user_role where id = 1);`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TTebeke2-1628668796577)(resource/1628600829263.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/785153314e4e450faba1eaa6c5e242bb.png)
DERIVED例子
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-pjIifU7U-1628668796579)(resource/1628601331935.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/62981ec2fb194536ac7ba1c34525b6f7.png)
UNION & UNION RESULT 例子
`explain select id from sys_user union select id from sys_role;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6uXW4FBY-1628668796580)(resource/1628601469854.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3dd677177ede450d81cb5bd0127bed09.png)
# 2.1.3.5 explain之type
| type | 含义 |
|---|---|
| NULL | 不访问任何表、索引,直接返回结果 |
| system | 表只有一行记录【系统表】 |
| const | 通过主键索引或者唯一索引,查找出一条记录 |
| eq_ref | 多表联查,关联的字段都是各自表的主键 |
| ref | 单表查询:使用唯一索引的前缀索引或非唯一索引的前缀索引或非唯一索引的全列索引进行查询。多表联合查询:关联的字段不是自己表的主键,是外键。 |
| range | 使用一个单列索引,或复合索引的前缀索引进行范围查询 |
| index | 从索引树进行查询 |
| all | 全表扫描 |
NULL例子
`explain select now();`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uZCJHEcw-1628668796582)(resource/1628602303396.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f24325b6ca87481c98a86998955fdba0.png)
const例子
`explain select * from sys_user where id=50;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-P3906PFH-1628668796584)(resource/1628602416735.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/643c2c01209548e88be4ac8161e9c09d.png)
eq_ref例子
`explain select * from sys_user u, sys_role r where u.id=r.id;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-MKUkEc58-1628668796586)(resource/1628602951372.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7855ca66bc1340d58c9a3bbc521cbf88.png)
ref例子
`create index idx_user_login_name on sys_user(login_name);
explain select * from sys_user where login_name = '机构管理员';`
* 1
* 2
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-UuS4Hj9p-1628668796588)(resource/1628603248700.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/11f66b8b497345c5b4d3b0d97dc0b1f8.png)
range例子
`explain select * from sys_user where id in (50,51,52);`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-i5MbeVb1-1628668796589)(resource/1628603341818.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ecbb06293f348e7a105d680411441d9.png)
index例子
`explain select id from sys_user;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZPTfxNes-1628668796592)(resource/1628603450923.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b2edb2d0127445d2b8f5b5029d2d9274.png)
执行效率排序
`NULL > system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > all`
* 1
# 2.1.3.6 explain之key
`possible_keys:可能用到的索引列表
key:实际使用的索引
key_len:索引字段的最大可能长度,并非实际使用长度【字节】`
* 1
* 2
* 3
# 2.1.3.7 explain之extra
额外信息
| extra | 含义 |
|---|---|
| using filesort | MySQL对数据使用一个外部的索引排序而不是按照表内的索引顺序进行读取,称为“文件排序” |
| using temporary | 使用临时表保存中间结果,MySQL在对查询结果排序时使用临时表。常见于order by group by |
| using index | 相应的SELECT操作使用了覆盖索引,避免回表 |
using filesort例子
`explain select * from sys_user order by password;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZfrTNNEM-1628668796594)(resource/1628604033980.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d732aa18b787461b9fc576611f2d30a1.png)
using temporary例子
`explain select * from sys_user group by password;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-GRsfoL8V-1628668796596)(resource/1628604201078.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2c0d1bd9725640d68babd4434284b279.png)
using index例子
`explain select username from sys_user order by username;`
* 1
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Z5K3DguB-1628668796600)(resource/1628604164025.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c68df76164244112928fe68109d7de1f.png)
# 2.1.4 show profile分析SQL
show profiles能够在优化SQL中帮助我们了解时间都耗费到哪里了
`-- 查看当前MySQL是否支持profile
mysql> select @@have_profiling;
+------------------+
| @@have_profiling |
+------------------+
| YES |
+------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
-- 查看当前是否开启了profiling
mysql> select @@profiling;
+-------------+
| @@profiling |
+-------------+
| 0 |
+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
-- 开启profiling【仅当前session】
mysql> set profiling=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
-- 进行查询操作
mysql> select * from user limit 20000,1
-> ;
+-------+----------------------+------+---------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | address | birthday |
+-------+----------------------+------+---------+---------------------+
| 20001 | v4Ep2zqXuVJnkIzlRhX9 | 75 | 广州 | 2020-09-30 12:14:05 |
+-------+----------------------+------+---------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user order by name limit 2000,1;
+--------+--------------------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | address | birthday |
+--------+--------------------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| 764557 | 03uH675cuPcinUmWna2xjQAFP2zxYF | 29 | 珠海市 | 2020-09-12 02:49:11 |
+--------+--------------------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
1 row in set (6.70 sec)
-- 使用show profiles
mysql> show profiles;
+----------+------------+-----------------------------------------------+
| Query_ID | Duration | Query |
+----------+------------+-----------------------------------------------+
| 1 | 0.00015600 | SELECT DATABASE() |
| 2 | 0.00548875 | select * from user limit 20000,1 |
| 3 | 6.69228925 | select * from user order by name limit 2000,1 |
+----------+------------+-----------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
-- 选择指定记录查看耗时
mysql> show profile for query 3;
+--------------------------------+----------+
| Status | Duration |
+--------------------------------+----------+
| starting | 0.000082 |
| Executing hook on transaction | 0.000005 |
| starting | 0.000009 |
| checking permissions | 0.000007 |
| Opening tables | 0.000034 |
| init | 0.000006 |
| System lock | 0.000010 |
| optimizing | 0.000005 |
| statistics | 0.000016 |
| preparing | 0.000022 |
| executing | 6.691968 |
| end | 0.000018 |
| query end | 0.000005 |
| waiting for handler commit | 0.000023 |
| closing tables | 0.000013 |
| freeing items | 0.000021 |
| logging slow query | 0.000033 |
| cleaning up | 0.000015 |
+--------------------------------+----------+
18 rows in set, 1 warning (0.03 sec)` ![][img-3]
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
* 51
* 52
* 53
* 54
* 55
* 56
* 57
* 58
* 59
* 60
* 61
* 62
* 63
* 64
* 65
* 66
* 67
* 68
* 69
* 70
* 71
* 72
- 支持进一步选择all、cpu、block io、context switch、page faults等查看其他信息
`mysql> show profile cpu for query 3;
+--------------------------------+----------+----------+------------+
| Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system |
+--------------------------------+----------+----------+------------+
| starting | 0.000082 | 0.000038 | 0.000037 |
| Executing hook on transaction | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0.000003 |
| starting | 0.000009 | 0.000004 | 0.000004 |
| checking permissions | 0.000007 | 0.000004 | 0.000004 |
| Opening tables | 0.000034 | 0.000016 | 0.000016 |
| init | 0.000006 | 0.000003 | 0.000003 |
| System lock | 0.000010 | 0.000005 | 0.000005 |
| optimizing | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0.000003 |
| statistics | 0.000016 | 0.000008 | 0.000007 |
| preparing | 0.000022 | 0.000011 | 0.000012 |
| executing | 6.691968 | 1.705168 | 0.784907 |
| end | 0.000018 | 0.000006 | 0.000006 |
| query end | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0.000002 |
| waiting for handler commit | 0.000023 | 0.000012 | 0.000012 |
| closing tables | 0.000013 | 0.000006 | 0.000006 |
| freeing items | 0.000021 | 0.000011 | 0.000011 |
| logging slow query | 0.000033 | 0.000017 | 0.000016 |
| cleaning up | 0.000015 | 0.000007 | 0.000008 |
+--------------------------------+----------+----------+------------+
18 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)` ![][img-4]
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
# 2.1.5 trace分析优化器执行计划
trace 用来对SQL进行跟踪,可以了解为什么优化器选择A计划而不是B计划
`-- 打开 trace,设置格式为JSON,设置最大使用内存
mysql> set optimizer_trace="enabled=on", end_markers_in_json=on;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> set optimizer_trace_max_mem_size=1000000;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 进行查询
mysql> select * from user where id <= 4;
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | address | birthday |
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
| 1 | Z7zEgyrL3PJq86sfhas3 | 26 | 云浮市 | 2019-01-13 10:04:55 |
| 2 | MrldItwPeb6VDk7zCOO1 | 2 | 汕尾市 | 2018-10-18 09:41:51 |
| 3 | 5ag8vXuMnV0JRBH2PKkG | 72 | 梅州市 | 2021-06-16 06:22:28 |
| 4 | SccWwgENpikMyriAdJ3V | 12 | 江门市 | 2019-01-17 15:21:14 |
+----+----------------------+------+-----------+---------------------+
-- 查看优化器执行计划
mysql> select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace\G;` ![][img-5]
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
``QUERY: select * from user where id <= 4
TRACE: {
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `user`.`id` AS `id`,`user`.`name` AS `name`,`user`.`age` AS `age`,`user`.`address` AS `address`,`user`.`birthday` AS `birthday` from `user` where (`user`.`id` <= 4)"
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_preparation */
},
{
"join_optimization": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"condition_processing": {
"condition": "WHERE",
"original_condition": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)",
"steps": [
{
"transformation": "equality_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)"
},
{
"transformation": "constant_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)"
},
{
"transformation": "trivial_condition_removal",
"resulting_condition": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)"
}
] /* steps */
} /* condition_processing */
},
{
"substitute_generated_columns": {
} /* substitute_generated_columns */
},
{
"table_dependencies": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"row_may_be_null": false,
"map_bit": 0,
"depends_on_map_bits": [
] /* depends_on_map_bits */
}
] /* table_dependencies */
},
{
"ref_optimizer_key_uses": [
] /* ref_optimizer_key_uses */
},
{
"rows_estimation": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"range_analysis": {
"table_scan": {
"rows": 1902939,
"cost": 192515
} /* table_scan */,
"potential_range_indexes": [
{
"index": "PRIMARY",
"usable": true,
"key_parts": [
"id"
] /* key_parts */
}
] /* potential_range_indexes */,
"setup_range_conditions": [
] /* setup_range_conditions */,
"group_index_range": {
"chosen": false,
"cause": "not_group_by_or_distinct"
} /* group_index_range */,
"skip_scan_range": {
"potential_skip_scan_indexes": [
{
"index": "PRIMARY",
"usable": false,
"cause": "query_references_nonkey_column"
}
] /* potential_skip_scan_indexes */
} /* skip_scan_range */,
"analyzing_range_alternatives": {
"range_scan_alternatives": [
{
"index": "PRIMARY",
"ranges": [
"id <= 4"
] /* ranges */,
"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,
"rowid_ordered": true,
"using_mrr": false,
"index_only": false,
"rows": 4,
"cost": 0.66107,
"chosen": true
}
] /* range_scan_alternatives */,
"analyzing_roworder_intersect": {
"usable": false,
"cause": "too_few_roworder_scans"
} /* analyzing_roworder_intersect */
} /* analyzing_range_alternatives */,
"chosen_range_access_summary": {
"range_access_plan": {
"type": "range_scan",
"index": "PRIMARY",
"rows": 4,
"ranges": [
"id <= 4"
] /* ranges */
} /* range_access_plan */,
"rows_for_plan": 4,
"cost_for_plan": 0.66107,
"chosen": true
} /* chosen_range_access_summary */
} /* range_analysis */
}
] /* rows_estimation */
},
{
"considered_execution_plans": [
{
"plan_prefix": [
] /* plan_prefix */,
"table": "`user`",
"best_access_path": {
"considered_access_paths": [
{
"rows_to_scan": 4,
"access_type": "range",
"range_details": {
"used_index": "PRIMARY"
} /* range_details */,
"resulting_rows": 4,
"cost": 1.06107,
"chosen": true
}
] /* considered_access_paths */
} /* best_access_path */,
"condition_filtering_pct": 100,
"rows_for_plan": 4,
"cost_for_plan": 1.06107,
"chosen": true
}
] /* considered_execution_plans */
},
{
"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {
"original_condition": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)",
"attached_conditions_computation": [
] /* attached_conditions_computation */,
"attached_conditions_summary": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"attached": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)"
}
] /* attached_conditions_summary */
} /* attaching_conditions_to_tables */
},
{
"finalizing_table_conditions": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"original_table_condition": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)",
"final_table_condition ": "(`user`.`id` <= 4)"
}
] /* finalizing_table_conditions */
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`user`"
}
] /* refine_plan */
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_optimization */
},
{
"join_execution": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
] /* steps */
} /* join_execution */
}
] /* steps */
}
MISSING_BYTES_BEYOND_MAX_MEM_SIZE: 0
INSUFFICIENT_PRIVILEGES: 0
1 row in set (0.01 sec)`` ![][img-6]
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
* 51
* 52
* 53
* 54
* 55
* 56
* 57
* 58
* 59
* 60
* 61
* 62
* 63
* 64
* 65
* 66
* 67
* 68
* 69
* 70
* 71
* 72
* 73
* 74
* 75
* 76
* 77
* 78
* 79
* 80
* 81
* 82
* 83
* 84
* 85
* 86
* 87
* 88
* 89
* 90
* 91
* 92
* 93
* 94
* 95
* 96
* 97
* 98
* 99
* 100
* 101
* 102
* 103
* 104
* 105
* 106
* 107
* 108
* 109
* 110
* 111
* 112
* 113
* 114
* 115
* 116
* 117
* 118
* 119
* 120
* 121
* 122
* 123
* 124
* 125
* 126
* 127
* 128
* 129
* 130
* 131
* 132
* 133
* 134
* 135
* 136
* 137
* 138
* 139
* 140
* 141
* 142
* 143
* 144
* 145
* 146
* 147
* 148
* 149
* 150
* 151
* 152
* 153
* 154
* 155
* 156
* 157
* 158
* 159
* 160
* 161
* 162
* 163
* 164
* 165
* 166
* 167
* 168
* 169
* 170
* 171
* 172
* 173
* 174
* 175
* 176
* 177
* 178
* 179
* 180
* 181
* 182
* 183
* 184
* 185
* 186
* 187
* 188
* 189
* 190
* 191
* 192
* 193
* 194
* 195
* 196
* 197
* 198
# 2.2 优化大批量插入
使用
load命令导入数据可以适当提高导入效率
- 对于InnoDB存储引擎表:
- 主键采用顺序插入,如果没有主键,InnoDB默认会自动创建一个内部列作为主键
- 关闭唯一性校验:导入前执行
set unique_checks=0,导入结束执行set unique_checks=1- 设置手动提交事务,导入前执行
set autocommit=0,导入后执行set autocommit=1
# 2.3 优化insert语句
合并insert语句:
优化前:
`insert into tb_test values(1, 'Tom'); insert into tb_test values(2, 'Cat'); insert into tb_test values(3, 'Jerry');` * 1 * 2 * 3优化后:
`insert into tb_test values(1, 'Tom'),(2, 'Cat'),(3, 'Jerry');` * 1
在事务中提交数据:
`start transaction; insert into tb_test values(1, 'Tom'); insert into tb_test values(2, 'Cat'); insert into tb_test values(3, 'Jerry'); commit;` * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5
数据有序插入:
优化前:
`insert into tb_test values(3, 'Tom'); insert into tb_test values(2, 'Cat'); insert into tb_test values(1, 'Jerry');` * 1 * 2 * 3优化后:
`insert into tb_test values(1, 'Tom'); insert into tb_test values(2, 'Cat'); insert into tb_test values(3, 'Jerry');` * 1 * 2 * 3
# 2.4 优化order by语句
# 2.4.1 过程
表存在的索引:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-vI5T4No0-1628668796604)(resource/1628641131176.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c3e4fd47bd2048009186b7c19625324a.png)
优化前:没有使用索引而是using filesort
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3Ef0KVhZ-1628668796606)(resource/1628641186369.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9409e6c7d653451095cb5cd3db6c19c5.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
优化后:使用using index【原理是覆盖索引】
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-NGefV0XZ-1628668796608)(resource/1628641231687.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1f910684fa41442f8d91fb54f3ceb9c9.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
当一个需要升序,一个需要降序时:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-gjkyx1IE-1628668796610)(resource/1628641361037.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c0272e27320e4e24bab79b883f55b0a5.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
总结:
- 选择字段与排序字段尽量满足
覆盖索引order by字段的顺序应和索引顺序相同,且要么都是升序要么都是降序
# 2.4.2 using filesort优化
知识储备:
MySQL的两个排序算法:
- 两次扫描算法:首先取出排序字段和行指针,然后在排序区【sort buffer】排序,完成排序后根据行指针回表读取记录。【若排序区不足,则在临时表中存储排序结果】可能导致大量的随机IO操作
- 一次扫描算法:一次性取出所需字段,在排序区排序后直接输出结果集,排序区内存开销大,但效率较高
MySQL通过比较系统变量
max_length_for_sort_date和Query语句取出字段总大小,来哦按段选择哪种排序算法。【max_length_for_sort_data更大则选择一次扫描,否则使用二次扫描】
优化:
适当提高
sort_buffer_size和max_length_for_sort_data系统变量,增大排序区的大小
`mysql> show variables like 'max_length_for_sort_data';
+--------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-------+
| max_length_for_sort_data | 4096 |
+--------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> show variables like 'sort_buffer_size';
+------------------+---------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+---------+
| sort_buffer_size | 1048576 |
+------------------+---------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
# 2.5 优化group by语句
优化前:
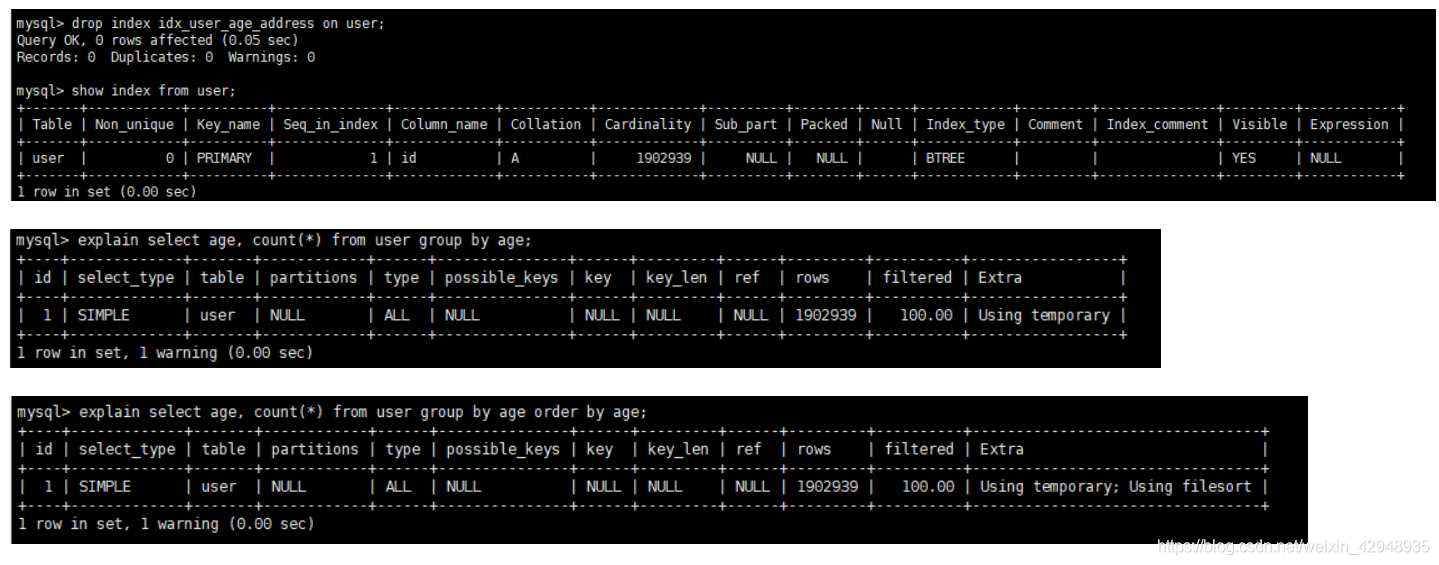
添加索引后:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yqrJuwm6-1628668796617)(resource/1628649714495.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/583d95760fd74e448ed8f155d5901c41.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 2.6 优化嵌套查询
优化前:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-VIgUZosj-1628668796621)(resource/1628649938300.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ad6a10f7fbf4ad2a1478d8157af509b.png)
优化方式:使用多表联查替换子查询
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QPDS9T6r-1628668796623)(resource/1628650000929.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9b96aa28c64541bda872fee303f41bbf.png)
# 2.7 优化OR条件
包含or的查询子句,需要每个or条件都用到索引,且不能使用到复合索引,否则索引失效进行全表扫描
优化前:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-oFAwlcss-1628668796626)(resource/1628650286966.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1c2e4d66eb8842d2bb8257256d6800bf.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
优化一,设置索引:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-rtOv0Cxd-1628668796627)(resource/1628650402087.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/00a892ee657f49dfa818f53743bc75d8.png)
优化二,使用Union:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8eprE2GF-1628668796629)(resource/1628650538794.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9efc3320d4864a6dbbc1763ff72d9948.png)
# 2.8 优化分页查询
一般分页查询通过创建覆盖索引能够获得比较好的性能。但是数据量过大时【百万级】当执行limit 1000000 10时,需要MySQL排序前1000010记录,但只返回1000000~1000010记录,其他丢弃,代价非常大
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XKZkNYXP-1628668796631)(resource/1628661168852.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/127f7d855d444ae2afc49c2e7d56558e.png)
优化一:在索引上完成排序分页操作,根据主键关联原表查询所需内容
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-OG4uQwUA-1628668796633)(resource/1628661383957.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ca554442d0e742f596b9e1433e793447.png)
优化二:把limit查询转换成某个位置的查询【仅适应主键自增表,且中间没有断层】
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Yq7wWLYp-1628668796634)(resource/1628661527734.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6e0d6961f1f84e489278ff21f73027c3.png)
# 2.9 使用SQL提示
通过显性SQL命令建议【强制】MySQL执行某些操作
# 2.9.1 USE INDEX
【建议MySQL使用哪个索引】
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-YnMHVzCO-1628668796636)(resource/1628662123308.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/55590cf5a64c4e02a43aad2fd4ff4e56.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 2.9.2 IGONRE INDEX
【建议MySQL忽略哪个索引】
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-I2wGj8QW-1628668796638)(resource/1628662233088.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8e70aa29d4de4294ab60fae4cfa7a1ed.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
# 2.9.3 FORCE INDEX
【强制MySQL使用哪个索引】
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-xjyN7vEX-1628668796640)(resource/1628662495378.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fa1c020290e042ee956ffcb93bc1ffcf.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
- 应用优化
- 使用数据库连接池
- 减少对MySQL的访问:
- 避免对数据进行重复检索。比如:
select id,name from user和select id,status from user可以合并为select id, name, status from user- 增加缓存层。比如使用
Redis或者ORM框架提供的缓存- 进行负载均衡:
- 利用MySQL主从复制实现读写分离
- 采用分布式数据库架构【分库分表】
- 内存管理优化
# 4.1 优化原则
- 在OS及其他程序正常运行的情况下,尽量多的给MySQL分配内存
- MyISAM存储引擎的数据文件读取依赖OS自身的IO缓存,故需要预留更多的内存给OS
- 排序区、连接区的缓存时分配给每个session专用的,其值的设置需要根据最大连接数合理分配
# 4.2 MyISAM内存优化
MyISAM存储引擎使用key_buffer缓存索引块,加锁索引读写。对于表则没有缓存机制,需要依赖操作系统的IO缓存
key_buffer_size:设置缓存块大小,建议至少1/4可用内存
`key_buffer_size=512M`
* 1
read_buffer_size:若需要经常顺序扫描表,可以增大该值,但是该值为session独占
read_rnd_buffer_size:需要做排序的表查询,可以适当增加该值,但是该值为session独占
# 4.3 InnoDB内存优化
InnoDB使用一块内存区作为IO缓冲池,用来缓存索引块和数据块
innodb_buffer_pool_size:决定最大缓存区大小,该值越大则命中率越高,磁盘IO操作越少
`innodb_buffer_pool_size=512M`
* 1
innodb_log_buffer_size:重做日志缓存的大小,对于可能产生大量更新记录的大事务,增加该值可以避免在事务提交前就执行不必要的日志写入磁盘的操作
`innodb_log_buffer_size=10M`
* 1
- 并发参数优化
MySQL Server是多线程结构的,包括后台线程和客户服务线程。其中控制并发连接和线程的主要参数为:max_connections、back_log、thread_cache_size、table_open_cache
# 5.1 max_connections
控制允许连接到MySQL的最大连接量。默认值151。如果状态变量connection_errors_max_connections不为0且一直增长,说明不断一连接请求因数据库连接数已达到最大而失败,这时可以考虑增加max_connections
MySQL最大可支持连接数取决很多因素:
- 给定OS平台的线程库质量
- 内存大小
- 每个连接的负荷
- CPU处理速度
- 期望的响应时间等
# 5.2 back_log
- 控制MySQL监听TCP端口时设置的积压请求栈大小。当连接数到达
max_connections,新来的请求会被存储在积压栈中等待。若等待数量超过back_log,则拒绝连接,并报错。- 5.6.6版本之前默认值为
50,新版本默认为50 + max_connections/5,最大不超过900
# 5.3 table_open_cache
- 控制所有SQL语句执行线程可以打开表缓存的数量
- 在执行SQL语句时,每个SQL执行线程至少要打开1个表缓存。
- 该参数的值应该根据设置的最大连接数
max_connections以及每个连接执行关联查询中设计的表的最大数量来设定:max_connections * N
# 5.4 thread_cache_size
为了加快连接数据库的速度,MySQL会缓存一定数量的客户服务线程以备重用。
# 5.5 innodb_lock_wait_timeout
设置InnoDB事务等待行锁的时间,默认值为50ms。
- 对于需要快速反馈的业务系统,可以设置小些,以免事务长时间挂起
- 对于后台运行的批处理程序,可以设置大些,以免发生大的回滚操作

![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aZK78PV4-1628668796562)(resource/1628579511132.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ebe515c5ee2443a9a57524e6b25cbb3.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KvfpG6de-1628668796564)(resource/1628579550205.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c8429a70d7a54067a84be0e43da9d492.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bSXVNvhy-1628668796570)(resource/1628580803599.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1f3458ee9bd74b408716c1e4a17019c6.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FeGabiEr-1628668796572)(resource/1628581151750.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3dd84e024e3d4650b9ee1230b9064d56.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-CK78he9R-1628668796574)(resource/1628581740579.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/afd08b428b4544ef855f6f9831d3ce34.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mMYuVM9A-1628668796602)(resource/1628639972616.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/14fb19a7f8f8431e9584c4e060892319.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80Mjk0ODkzNQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)